Jenner was an English doctor, the pioneer of smallpox vaccination and the father of immunology.
He was born in Berkeley, Gloucestershire on 18 May 1749, the son of the local vicar.
At the age of 14, he was apprenticed to a local surgeon and then trained in London. In 1772, he returned to Berkeley and spent most the rest of his career as a doctor in his native town.
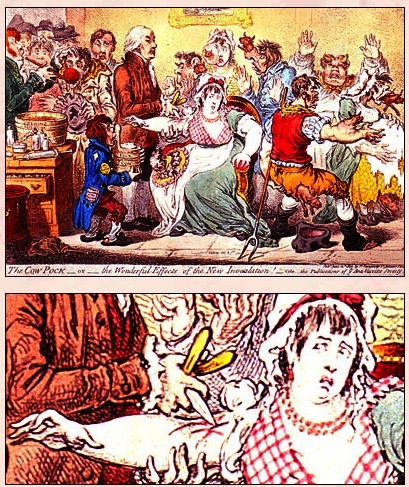
In 1796, he carried out his now famous experiment on eight-year-old James Phipps. Jenner inserted pus taken from a cowpox pustule and inserted it into an incision on the boy’s arm. He was testing his theory, drawn from the folklore of the countryside, that milkmaids who suffered the mild disease of cowpox never contracted smallpox, one of the greatest killers of the period, particularly among children.
Jenner subsequently proved that having been inoculated with cowpox Phipps was immune to smallpox.
He submitted a paper to the Royal Society in 1797 describing his experiment but was told that his ideas were too revolutionary and that he needed more proof. Undaunted, Jenner experimented on several other children, including his own 11-month-old son. In 1798, the results were finally published and Jenner coined the word vaccine from the Latin ‘vacca’ for cow.
Jenner was widely ridiculed. Critics, especially the clergy, claimed it was repulsive and ungodly to inocculate someone with material from a diseased animal. A satirical cartoon of 1802 showed people who had been vaccinated sprouting cow’s heads. The obvious advantages of vaccination and the protection it provided won out and vaccination soon became widespread.
Jenner became famous and spent much of his time researching and advising on developments in his vaccine. Jenner carried out research in a number of other areas of medicine and was also keen on fossil collecting and horticulture.
Vaccination provided immunity for up to ten years. Because war always spread smallpox, governments encouraged recruits to be vaccinated. In 1807, the Bavarians became the first to require recruits to be vaccinated and the practice of vaccination spread with the practice of war.
He died on 26 January 1823.