- Corporations and trusts begin to accumulate large capital reserves, ushering in Era of Big Business
- Western frontier rapidly parceled out and populated; Native Americans forced to assimilate and/or relocate
- Reconstruction policies leave African Americans behind in South as post–Civil War recovery continues
- Development of cities fueled by immigration and rise of business
1878 Timber and Stone Act opens land in California, Oregon, Nevada, and Washington to purchase by settlers
Exoduster migration of black communities to Kansas to escape Democratic control of South after the end of Reconstruction
Bland-Allison Act requires purchase of silver by treasury
Women’s suffrage amendment introduced in Congress after work by activist Susan B. Anthony; Senate does not vote on it until 1884
1879 Thomas Edison invents the electric light
White settlers begin to descend upon Native American reservations in Oklahoma, clamoring for land
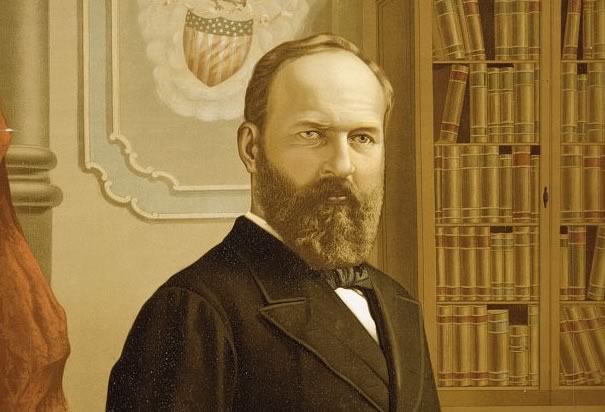
1880 James Garfield elected 20th president
British charitable organization Salvation Army starts work in United States
1881 Disappointed office-seeker Charles Guiteau assassinates Garfield; Vice President Chester A. Arthur becomes 21st president
Booker T. Washington becomes principal of Tuskegee Institute in Alabama, which provides vocational training to blacks
Henry James publishes novel The Portrait of a Lady
Federal trademark laws instituted to protect patent holders, encourage innovation
1882 Chinese Exclusion Act bans Chinese immigration for 10 years
John D. Rockefeller forms Standard Oil Trust
National time zones established
Brooklyn Bridge completed, speeding already rapid growth of New York City
Supreme Court declares Civil Rights Act of 1875 unconstitutional
Northern Pacific Railroad between Chicago and Seattle completed
1883 Pendleton Civil Service Act counters patronage, reforms U.S. government’s corrupt hiring practices
1884 Grover Cleveland elected 22nd president
Mark Twain publishes novel The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn
1885 Violent anti-Chinese riots occur in Rock Springs, Wyoming, and Tacoma, Washington
1886 Haymarket riot occurs when Chicago police disperse striking union workers demanding 8-hour workday; 7 policemen killed, 4 protesters sentenced to death; union movements nationwide suffer as a result
American Federation of Labor (AFL) formed to salvage labor movement; Samuel Gompers acts as leader until 1924
Chiricahua Apache leader Geronimo deported to Florida as prisoner of war
Wabash v. Illinois ruling holds that only federal government can regulate trade between states
1887 Interstate Commerce Act establishes federal commission to regulate trade between states
Dawes Severalty Act denies tribal rights, advances policy of forced assimilation and integration upon Native Americans; reduces tribal land claims sharply
Low rail fares encourage mass relocation of Midwesterners to Los Angeles
United States acquires naval rights at Pearl Harbor in Hawai‘i
1888 Benjamin Harrison elected 23rd president
1889 North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington admitted to Union as 39th, 40th, 41st, and 42nd states
Oklahoma land rush transfers more than two million acres of native-held land to white settlers
Jane Addams founds Hull House to provide relief to Chicago poor
Motion-picture camera invented
1890 Idaho and Wyoming admitted to Union as 43rd and 44th states
Congress establishes Oklahoma Territory, further stripping Native Americans of land claims in region
Federal forces massacre more than 200 Sioux at Wounded Knee
Congress establishes Yosemite National Park in California
Mississippi Plan levies poll tax, effectively disenfranchising black voters
Sherman Antitrust Act outlaws monopolies, price-fixing, other trade restraints
Sherman Silver Purchase Act is passed
U.S. Census Bureau announces frontier officially closed
McKinley Tariff raises duties on imports, strengthening U.S. businesses
1891 Forest Reserve Act allows president to set aside western lands for federal control, limiting private claims
Populist Party formed; composed primarily of western farmers
Electric trolleys begin to replace horses as primary mode of public transportation
1892 Geary Act extends Chinese Exclusion Act by 10 years, requires existing Chinese-American citizens to register with government
Steelworkers strike in Homestead strike against Carnegie Steel; Pinkerton Detectives called in to break strike; 10 people killed in riot
Dawes Act opens more than two million acres of Crow lands in Montana to white settlement
Grover Cleveland elected 24th president
1893 Panic of 1893 leads to a four-year period of financial instability
Six million acres of Cherokee land in Oklahoma opened to white settlement
Great Northern Railroad completed
Sherman Silver Purchase Act repealed
World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago celebrates 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus’s voyage to New World
1894 Carey Act grants more than one million acres of land to western states on condition of irrigation and resale to settlers
Pullman Strike, led by labor organizer Eugene V. Debs, cripples railroads nationwide; federal troops called on to restore order
Wilson-Gorman Tariff reestablishes high tariff levels after cuts
Coxey’s Army of 500 unemployed citizens marches on Washington, D.C., demanding relief for destitute and unemployed
1895 Booker T. Washington gives Atlanta Compromise speech at Cotton States Exposition, urging African Americans to accept second-class-citizen status in exchange for civil rights and equal education
Publishers William Randolph Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer compete for readership through practice of sensationalistic yellow journalism
U.S. v. E.C. Knight Co. ruling effectively disables Sherman Antitrust Act
1896 Utah admitted to Union as 45th state
Plessy v. Ferguson ruling repeals Civil Rights Act of 1875, upholding constitutionality of separate but equal services
William Jennings Bryan makes “Cross of Gold” speech at Democratic National Convention in Chicago, urging free coinage of silver and other Populist reforms
William McKinley elected 25th president
1898 Louisiana establishes grandfather clause for voting rights, placing literacy and property requirements on blacks but excusing whites from similar standards
Holden v. Hardy ruling upholds work hour limits for miners
USS Maine sinks in Havana Harbor, Cuba; U.S. press and public blame Spain
Spanish-American War takes place; Teddy Roosevelt leads Rough Riders in Battle of San Juan Hill in Cuba; United States crushes Spain in naval battles
Treaty of Paris ends Spanish-American War; United States annexes Guam, Philippines, and Puerto Rico
United States annexes Hawai‘i
Teller Amendment declares Cuba independent from Spain by U.S. authority
1899 United States announces Open Door Policy to gain foothold in Chinese markets
Cumming v. County Board of Education ruling declares laws establishing separate schools for white students constitutional even if comparable schools are not available for black students
1900 International forces quell Boxer Rebellion against Western imperialism in China
Criminalization of lynching proposed in Congress but fails in committee
McKinley reelected president
Foraker Act grants Puerto Rico limited degree of self-government
Gold Standard Act declares paper money backed by gold reserves
Credits: Sparknotes