John Thomas was born in Gloucester and after an apprenticeship as a stone mason came to the attention of the architect Sir Charles Barry. He worked on Buckingham Palace and the Palace of Westminster.He was put in charge of the carvings on the Palace of Westminster and worked prolifically on all kinds of sculpture, executing reliefs on structures as different as Balmoral Castle and Euston Station.
He became a major figure of the day, and was visited in his studio by the Queen and Prince Albert. He was described by Prince Albert as “a man of consummate ability without conceit or arrogance” (from the Illustrated London News, quoted in the Oxford Dictionary of National Biography).
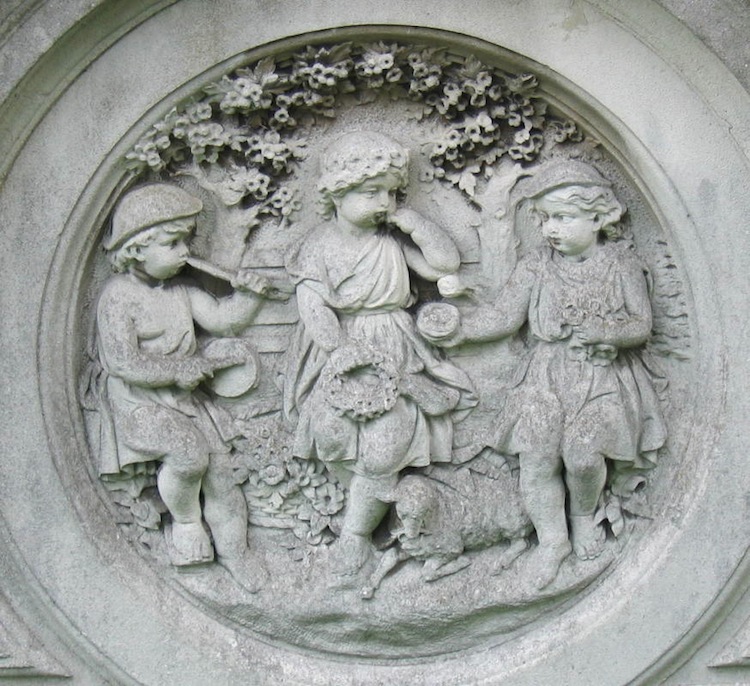
One of his many projects was the decorative stonework on the Italian Garden in Kensington Gardens.
Apprenticed to a stonemason after being left an orphan, he later went to Birmingham where his elder brother William Thomas (architect) was an architect. He was noticed by Charles Barry who immediately employed John Thomas as a stone and wood carver on Birmingham Grammar School (now demolished), his first collaboration with Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin.
Barry later appointed him the Supervising Carver on the Palace of Westminster in London, on which he is responsible for all the figures of English kings and queens. His work ‘Charity’ was shown at the Great Exhibition of 1851, and then adapted to form a memorial in Christ Church, Chalford, to his brother Richard who died in 1852.
His final work was the colossal statue of William Shakespeare displayed at the 1862 International Exhibition. A dispute over its placement hastened his death in April 1862, and he was buried in Kensal Green Cemetery, London. His massive (30 ft. high and 40 ft (12 m). in diameter) majolica fountain, also on display at the 1862 exhibition, was placed outside the V&A Museum of Childhood until it was demolished in 1926.
Thomas died not long afterwards, his death apparently hastened by a dispute over his huge statue of Shakespeare for the Great Exhibition of 1862.
Works
- Pastoral Scene with Putti, Italian Garden, Kensington Gardens, London
- Stone Urns and Water Nymph, Italian Garden
- Entwined initials of Victoria and Albert, Italian Garden
- Prince Albert, (bas relief), Italian Garden
Other work includes:
- A replica of the Bristol High Cross, which was erected in 1851.
- Eight allegorical statues at the 1847 Euston railway station representing the cities served by the line: London, Liverpool, Manchester, etc.
- Statue of Hugh Myddleton at Islington Green, London.
- Statue of Godiva, held in Maidstone Museum & Art Gallery
- The Atlas Fountain at Castle Howard
- Four British lions at each corner of the Britannia Bridge crossing the Menai Strait between the island of Anglesey and the mainland of Wales
- extensive friezes and spandrel figures for the Lloyds Bank, Bristol
- Carving and statues on Halifax Town Hall, created ca.1860-1862 in collaboration with Edward Middleton Barry to design of Charles Barry. Thomas carved three statues for the tower, but died before completing the fourth, which was overseen by another artist to his design.
As architect:
- Headington Hill Hall
- Somerleyton Hall